Usage
Out of the box, Rock allows files to be stored either as BLOBs (Binary Large Objects) in the database or as files on the web server. For many organizations, this is more than sufficient. Some, however, may prefer to store files in cloud storage, such as Amazon S3. This approach provides additional redundancy and offloads file storage from the web server.
When a file is requested, Rock’s GetFile.ashx handler proxies the file stream from Amazon S3, allowing files to be served securely through Rock as expected.
If needed, you can also link directly to the file in Amazon S3 using Lava. An example of this syntax is shown below:
{{ Person | Attribute:'EmploymentApplication','Url' }}
Storage Provider Setup
Once the package is installed, a new storage provider named Amazon BLOB Storage will appear under Admin Tools > System Settings > File Storage Providers. This provider is inactive by default and requires additional configuration before it can be enabled.
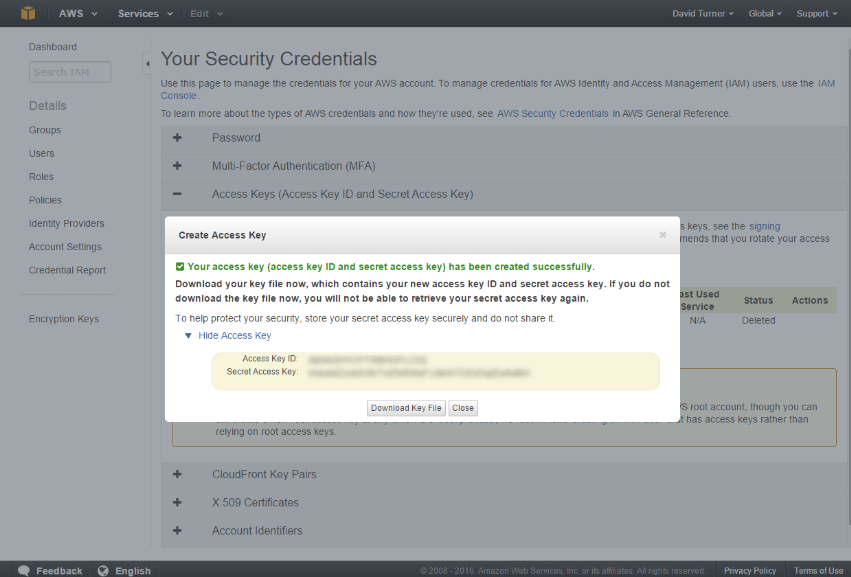
To configure this provider, you will need the Account Name and Access Key from your Amazon storage account. The location of these settings in Amazon is shown below.
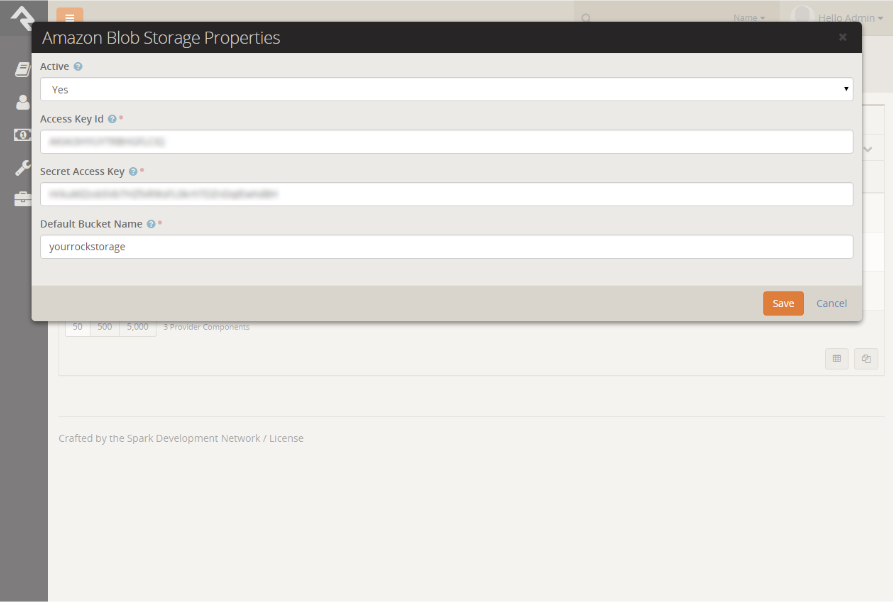
- Active: Determines whether this storage provider is active.
- Access Key ID: The access key ID from the Amazon account.
- Secret Access Key: The secret access key from the Amazon account.
- Default Bucket Name: The default Amazon S3 bucket used to store files.
Binary File Type Setup
Now that the storage provider is configured, you can set up file types to use it. To create a new file type, navigate to Admin Tools > General Settings > File Types.
When adding a new file type, there are three additional settings to be aware of.
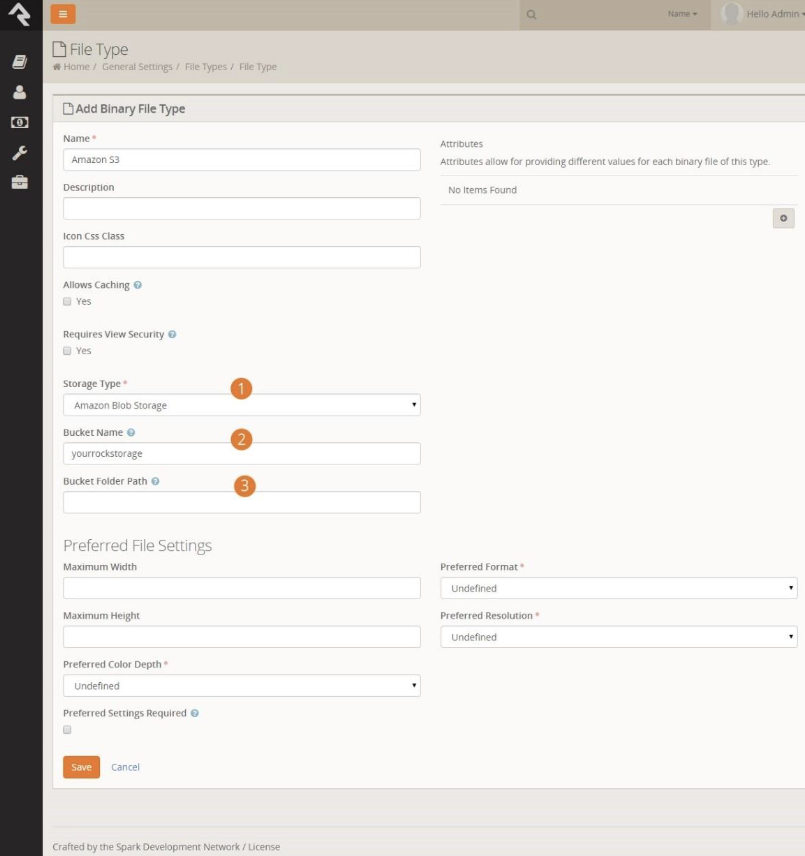
- Storage Type: Set this to Amazon BLOB Storage.
- Bucket Name: The Amazon S3 bucket you would like to use.
- Bucket Folder Path: The folder path within the bucket where files will be stored.
Once the file type(s) are set up, you can configure your attributes to use them just like you would with any other storage provider.